Impact of COVID-19 on the UK aviation industry – British Airways
Author: Jamie Walker
At: July 19, 2023
Abstract
Aim and Objectives: The aim of this study was to examine the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry research. In response to the above aim. The first objective of this study was to examine the theoretical concept pertaining to COVID-19 pandemic. The second objective of this review was to assess the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19. The third objective of this study was to analyse the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways. The final objective of this investigation was to provide recommendations for minimising the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the aviation sector of the UK.
Methodology: The current study used the qualitative design of research as the study aims to examine the impact of COVID-19 on British Airways as part of the UK aviation industry through multiple perceptions that are attained from representatives of the UK’s aviation industry. The primary data was collected via interviews with industry employees working at British Airways. The sample size chosen for the study was 10. The interviews were conducted on Skype/Zoom platforms considering the COVID-19 situation. The results were generated using the technique of thematic analysis
Findings: The findings reflected that the epidemic has disrupted years of growth at British Airways and the wider aviation sector, culminating in flight disruptions and long-term recession. Customers’ opinions have altered as a result of the COVID-19 troubles, travel bans, and the subsequent economic downturn, leading to a significant reduction in demand for air transport.
Recommendations: In terms of primary recommendations, it was advised to UK-based aviation businesses to postpone large-scale layoffs or changes to employment terms and benefits, as it is possible that the UK government’s proposals to revive and recover the sector would demonstrate favourable financial forecast for the aviation firms in the near future. Another recommendation was British Airways must prolong its discussion time so that all stakeholders may evaluate the planned workforce adjustments in light of the Government’s intentions to assist the aviation industry begin and thrive, as required by law.Key Words: COVID-19, Airline Sector, UK Aviation Sector, British Airways, Thematic Analysis, Qualitative Research, Open-Ended Interviews.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Contextual background
Pandemics are described as an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region (Rebmann et al., 2013). There have been different forms of pandemics (such as H1N1 virus, H2N2 virus, H3N2 virus and H1N1 pdm09 virus) that have had an impact on the world. Supporting the notion, Li and Mutchler (2020) elucidated that pandemics tend to have devastating impacts in the area of economic and social aspects. Apart from millions of people that are below the poverty line being affected severely, there are many privileged people also that are affected by pandemics. Qiu et al. (2017) asserted that businesses are another aspect that is heavily impacted by pandemics. The consumer behaviour and preferences start to change rapidly, which starts affecting businesses too (Kelly-Cirino et al., 2019). Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has started to affect the world, with businesses seeing the closure of their operations. One industry that has been severely impacted is that of the aviation industry in the United Kingdom. According to the research of Gössling, Scott and Hall (2020); Fernandes (2020), the global pandemic of COVID-19 has greatly affected multiple industries across the world. The study by Wire (2020) specified that COVID-19 resulted in the closure of borders and restrictions on local as well as international travelling, due to which the aviation industry of the UK has been affected. Furthermore, the report of Brunel.ac.uk. (2020) contemplated that the global pandemic of COVID-19 has reduced the demand for air travel by 14% in February 2020. Hence, the current research is based on examining the impact of COVID-19 on Aviation Industry of the UK, specifically British Airways.
1.2 Problem statement
According to Cox et al. (2020), pandemics have always been a cause of concern for people around the world, whether it is considered in terms of personal aspect or professional aspect. Majorly, pandemics tend to affect businesses around the world, causing many businesses to shut down operations, which is the situation with the COVID-19 pandemic. In this study, British Airways has been facing severe issues due to the COVID-19 pandemic forcing the organisation to opt for measures that would help it effectively run operations. Barry (2020) contemplated that the pandemic situation of COVID-19 has also affected consumer behaviour and preferences as people are not preferring to opt for less travelling and staying indoors. In this study, the issue of consumer behaviour and consumer preferences has become a cause of concern for British Airways as the corporation is witnessing less travelling of people, affecting their economic aspect as well. The study will assess the impact of COVID-19 on the aviation industry, with a specific focus on British Airways.
1.3 Research Aim
The study aims to examine the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry. The current study considered British Airways for analysing the impact of COVID-19 on the Aviation Industry of the UK.
1.4 Research Objectives
The research objectives of the study are:
- To examine the theoretical concept pertaining to COVID-19 pandemic.
- To assess the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19.
- To analyse the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways.
- To provide recommendations for minimising the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Aviation Industry of the UK.
1.5 Research Questions
The research questions of the study are:
- What is the COVID-19 pandemic?
- What are the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19?
- What are the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways?
1.6 Significance of the study
The present study aims to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry, with a specific focus on British Airways. Joy (2020) asserted that the pandemic usually creates a situation for businesses in which they have to create new strategies that would help them to deal with relevant situations effectively. This study would ensure that appropriate measures are stated to allow the aviation industry to implement specific strategies that would help the industry in dealing with the pandemic in such a way that the economic and social impacts are significantly improved. The study will benefit the people that are working in the aviation industry, specifically British Airways management. The British Airways management would be benefitted from the study in the sense that they would get an idea of how the management can provide better services to customers by analysing their behaviour and preferences changes that have occurred in light of the COVID-19 pandemic situation.
1.7 Structure of the study
The study comprises of five chapters, each of which is described below:
Chapter one is an introduction chapter. The chapter is focused on the background of the topic, problem statement, research aim, objectives and research questions, along with focusing on the significance of the study. Chapter two is a literature review chapter. The chapter comprises theoretical frameworks and concepts that are laid out in light of the research aim and objectives of the study. Extensive research is conducted on the main variables of the study to provide the reader with a broad view of the relevant aspects.
Chapter three is a methodology chapter. The chapter includes the method processes that will be used for successful competition of the study. The research philosophy, research approach, research strategy, data collection, sample size, data analysis and ethical considerations are discussed and justified for being made part of the study.
Chapter four is an analysis and discussion chapter. The chapter includes data that is gathered as per the method mentioned in the previous chapter, and a discussion is conducted in light of the aim and objectives of the study. Chapter five is a conclusion and recommendations chapter. The chapter is the final chapter of the study comprising of final observations and investigations made by assessing the significant discoveries of the study. The assessment will be written considering the achievement of the research aim and objectives. The researcher will also provide recommendations to improve the study.
CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
In this chapter of the study, the literature review is discussed, considering the research aim and objectives. The COVID-19 pandemic is a phenomenon that has affected businesses and people around the world, forcing every aspect to change their way of living as well as conducting operations (Donthu and Gustafsson, 2020). The aviation industry of the UK has been facing the negative effects of COVID-19, creating issues for organisations (such as British Airways) in the industry.
2.2 COVID-19 Pandemic
The research of Walker et al. (2020) contemplated that COVID-19 is an emerging virus that has been spread in almost every part of the world. The same researcher added that the global pandemic of COVID-19 has created a serious threat to the health of humans as it primarily affects the respiratory system of humans (Walker et al. 2020). Maneenop and Kotcharin (2020) demonstrated that the COVID-19 pandemic is considered to be the greatest challenge that the world has faced since World War 2. Since its emergence in Asia in 2019, the virus has spread to every continent except Antarctica. Apart from being a major health crisis, the pandemic is also observed to be an unprecedented socio-economic crisis (Nižetić, 2020). The author further stated that there has been severe social (the social life of people has decreased significantly), economic (people losing jobs and income) and political (governments are not implementing strict lockdowns and allowing businesses to be operated as usual) effects that have left deep and lasting scars on the world, as a whole.
2.3 Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Businesses
Ozili and Arun (2020) outlined that the COVID-19 pandemic has been having a severe impact on businesses, in the sense that bankruptcy is occurring for businesses, forcing a shutdown to take place. Some corporations in the United States, such as Sears, JCPenney, Neiman Marcus, Hertz and J. Crew, have come under severe financial pressure, and there is a chance that they might have to close down their businesses. Henriques (2020) elucidated that since the announcement of the COVID-19 pandemic measure of lockdown by countries around the world, it is imperative to note that businesses have been affected severely. There has been an 86% drop in revenues of businesses around the world due to the direct impact of the outbreak, in which 33% of businesses have predicted a further drop. However, Serrano and Kazda (2020) contemplated that COVID-19 has created an atmosphere in which business that is functioning online has been impacted positively. E-commerce business has seen a stark increase as people have started to shift to the online medium of purchasing and selling products and services. Supporting the notion, Amankwah-Amoah (2020) identified that COVID-19 cannot be considered troublesome for everyone, as all e-commerce businesses feel that this particular business has shifted consumer preferences towards the online sealing and buying of products and services. This is an area that was not used much by people before and has been in demand since the lockdown has been in implementation in various counties (such as the UK, US, China and Australia)
Nicola et al. (2020) asserted that apart from major business, there are expos, conferences, and large gathering and cultural establishment (galleries and museums) that has been called off due to the pandemic situation. The travel industry has been severely impacted, with 80% of hotel rooms being empty, airlines being forced to cut their workforce by 90% and tourism destinations seeing no profit in the year 2020. The study by Guo et al. (2020) highlighted that the pandemic of COVID-19 has created serious challenges for multiple industries as it primarily forced people to maintain social distancing and minimise physical contact. Additionally, the research of Fernandes (2020) asserted that the aviation industry is among the few industries that have been highly affected by the global pandemic of COVID-19 as multiple governments have restricted local as well as international travel.
2.4 Challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK owing to the global pandemic of COVID-19
The aviation industry of the UK has been highly prone to the COVID-19 outbreak, as the major airline British Airways has to cut around 12000 jobs to recover the loss that has been incurred during the outbreak of COVID-19 (Jolly, 2020). Furthermore, according to Amankwah-Amoah (2020), severe drops in the frequency of travellers have contributed to flight cancellations or unoccupied airplanes travelling across airports, resulting in significantly reduced airline revenues and forcing several airlines to cut off personnel or declaring insolvency. In order to reduce their losses, some airlines have tried to stop refunding cancelled flights while other airlines have laid-off airport operations and aircraft manufacturers to save their operational costs (Sharma and Nicolau, 2020).
As per the opinion of Nižetić (2020), the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in late 2019 created extensive risk for the global population and obstructed the operations of international business in multiple industries. In addition, the airline industry is among the first sectors that have been affected by the event since the disease is easily transmitted among individuals (Nicola et al., 2020). Until now, there has been no approved medical treatment for the condition, causing widespread anxiety among the British public. As a result, authorities all over the world have outlawed cross-border travel, reducing the aviation industry’s entire market value (Ozili and Arun, 2020).
As cited by Brunel.ac.uk. (2020), British Airways has been regarded as one of the largest airline firms, which was severely affected due to the unanticipated event of COVID-19 that restricted the aviation sector of the UK from allowing any air travel. In order to recover the negative impact of COVID-19 on the UK’s aviation sector, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), alongside the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), has introduced productive measures to protect the health and safety of passengers, crew and other airport staff to help the sustainable recovery of the airline industry (Gössling, Scott and Hall, 2020). The aforementioned study highlighted that hand hygiene, face masks, social distancing, temperature control, reduced aircrew and washing and disinfection have become essential interventions to be followed by the UK aviation industry to operate sustainably in the airline sector.
However, Singh et al. (2020) contemplated that there are people who still do not take the COVID-19 pandemic seriously and tend to move freely. The interventions that have been implemented in the UK aviation industry can only be considered successful if people abide by the standard operating procedures (SOPs) that have been set in place by the industry. According to Sharma and Nicolau (2020), the aviation industry in the UK has been facing resistance in terms of making people abide by SOPs because there are individuals that are not taking the COVID-19 pandemic seriously. People still believe that the COVID-19 pandemic is a hoax that has been created by the government to pressurize people to stay at home (Bambra et al., 2020; Tan et al., 2020). This has created further issues for the aviation industry as they are strictly told by the government to not allow anyone into the airport if they are not following the SOPs.
2.5 COVID-19 Impact on consumer behaviour and consumer preferences in the aviation industry
According to Nhamo, Dube and Chikodzi (2020), one of the major changes that have occurred due to the COVID-19 pandemic is related to consumers. The authors further stated that there has been a significant impact of COVID-19 on consumer behaviour and preferences. Due to the economic situation of the UK on the decline and people losing jobs at a rapid speed, consumer behaviour and preferences has also changed. Supporting the notion, Ye, Ji and Barthelemy (2020) stated that people have become more conscious about they spend their money. Although consumers are continuing to purchase the basic needs that are required for survival, the shopping and travelling aspect have taken a hit. Consumers have dropped the idea of travelling abroad and spending a huge amount on tickets and hotel bookings. Goodell (2020) outlined that the COVID-19 pandemic has forced many organisations in the aviation industry to increase their ticket prices so that they can meet their monthly goal. This particular aspect has not settled well with people, as stated by Jones and Comfort (2020). Consumer behaviour has witnessed a sharp change, with people now thinking twice if they want to spend money on a trip that is not required at the moment and can wait for some time until the COVID-19 pandemic is completely gone. Additionally, Sukri et al. (2020) pointed out that tourist destinations have also witnessed a significant decline as people have started to cancel their trips due to the fear of COVID-19. According to Tay et al. (2020), consumer preferences have changed owing to COVID-19, in the sense that there has been a decrease in holiday spending. This particular notion is being witnessed in countries that have shown signs of recovery.
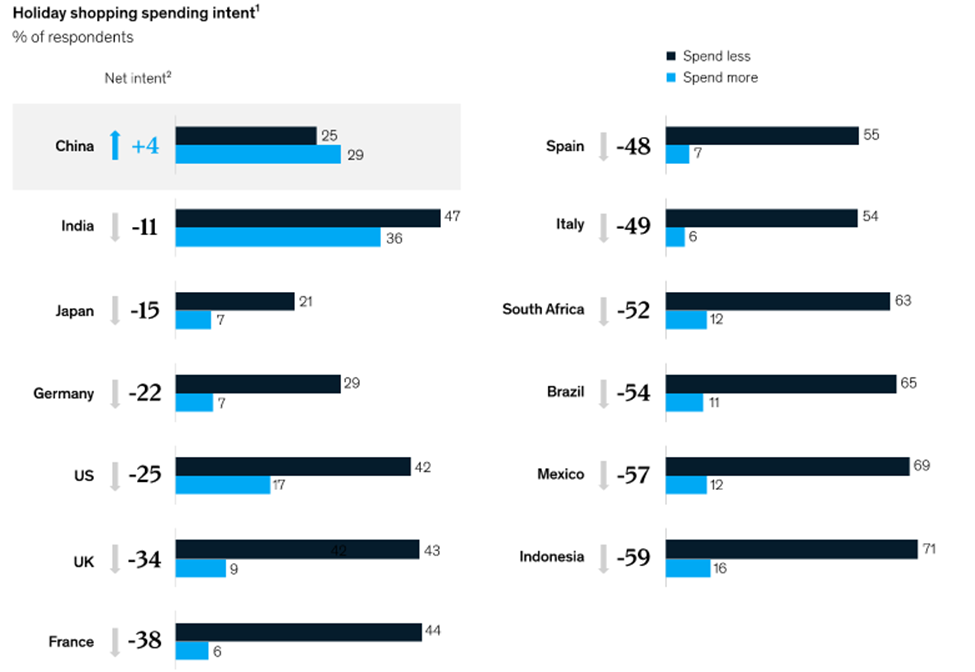
Figure 1 – Holiday spending (Source – McKinsey & Company, 2020)
It can be observed from the above figure, the except for China, consumers in the rest of the countries have significantly dropped their holiday spending plans due to the pandemic situation. There has been a 34% decrease in the UK regarding holiday spending, with people opting to spend less or nothing until the pandemic situation is resolved. Moreover, Roy (2020) stated that in the aviation industry, this particular trend is being perceived as a negative aspect because it means that the industry would suffer further loss and will take more time to recover from it, even in the post-pandemic situation. According to Bureau (2020), consumer behaviour has changed in the sense that people are fearful of their lives as the virus spread within the proximity of 6 feet. Due to this, people are avoiding travel altogether.
2.6 Literature gap
There have been studies on the COVID-19 pandemic (such as Kumar, 2020 and Amankwah-Amoah, 2020) and how it has affected businesses worldwide. Different industries have been severely impacted due to COVID-19 as there has been no business taking place, people are not purchasing or selling any products or services, and any cross-country business has been completely shut down at present. On the other hand, there have been studies of previous pandemics impacts on the aviation industry (such as Vinod, 2020 and Singh et al., 2020) which has caused the aviation industry to suffer losses and not be able to make any revenue or profit. Moreover, the aviation industry has also witnessed the situation of cutting down jobs leading to people being unemployed.
There are studies on the impact of a pandemic on consumer behaviour and consumer preferences (such as Czerny et al., 2020 and Nhamo, Dube and Chikodzi, 2020) that shows the importance of consumer behaviour and consumer preference on businesses, forcing them to change their strategies accordingly. It is imperative to note that there have been cases when organisations had to close their operations because consumers did not prefer to spend money on products and services that they felt were not worthy of being attained during the specific pandemic. However, there is a significant literature gap in the area of COVID-19’s impact on the aviation industry in the United Kingdom. By conducting the current study, the researcher will focus on fulfilling the literature gap and assessing how COVID-19 has impacted the aviation industry of the UK, considering consumer preferences and consumer behaviour.
2.7 Chapter Summary
In this chapter of the study, a literature review was discussed in light of the research aim and objectives. It has been observed from the gathered literature that the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the aviation industry has been a severe one. The industry has been facing severe issues, in terms of cancelled flights, people not travelling to other countries for holiday purposes, any form of domestic travelling has also been cancelled, among other aspects. Additionally, consumer preferences and consumer behaviour have also had an impact on the aviation industry as due to the fear of the pandemic, people are scared to travel as they feel that due to physical interaction, the virus might spread. This has created further issues for the aviation industry.
CHAPTER 3: METHODOLOGY
3.1 Introduction
In this chapter of the study, the methodology chapter has been discussed. The chapter comprises of research philosophy, research approach, research design, data collection, sample size, data analysis, research limitations, and ethical considerations.
3.2 Research philosophy
Van de Ven and Poole (2017) demonstrated that research philosophy emphasises on the source, nature and development of the information. The notion here is to focus on the belief regarding the ways the data related to a phenomenon should be gathered, assessed and then used in the study. There are four types of research philosophy, which are pragmatism, positivism, realism and interpretivism. For this study, interpretivism was used. Park and Park (2016) asserted that interpretivism helps researchers to interpret elements of the study by making human interest as part of the study. The justification for using interpretivism in this study is that the researcher is looking to get views from people that are part of British Airways to know how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the company’s business. The human elements here will help the researcher in forming better observations.
3.3 Research approach
Chu and Ke (2017) described the research approach as a set of plans and procedures for the research that helps in setting out broad assumptions related to the methods of data collection, analysing the data and then interpreting it. There are three types of research approaches which are deductive, inductive, and abductive. For this study, the inductive approach was used. Dougherty (2017) identified that the inductive approach helps in attaining reasoning, which helps in reaching the final observation. The researcher focuses on a series of patterns and develops an explanation for the specific patterns that are in line with the topic of the study. The justification of using the inductive approach is that the researcher is looking to identify patterns and relationships from the information that would be attained from people that are part of British Airways.
3.4 Research design
According to the research of MacDonald (2012), there are three types of study techniques used by academics all around the globe that are entitled as quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method research. The study of Jamshed (2014) asserted that a quantitative method of research is based on showcasing facts and figures with logical justification for presenting the findings of the study. While the study of Mackey and Gass (2015) stated that the qualitative method focuses on a subjective point of view and employs critical argumentation to present the finding on the phenomena. The current study used the qualitative methodology of research as the study aims to examine the impact of COVID-19 on British Airways as part of the UK aviation industry through multiple perceptions that are attained from representatives of the UK’s aviation industry.
3.5 Data Collection and sample size
Bertrand and Hughes (2017) elucidated that data collection is the procedure of gathering information from sources that are relevant to the topic of the study in answering the research problem. There are two forms of data collection methods, which are primary and secondary. For this study, the primary qualitative research method was used. Adler et al. (2017) demonstrated that primary qualitative research comprises words, sounds, feelings, emotions and elements that are non-quantifiable. The justification of using the primary qualitative data collection is that it helped the researcher in gaining an in-depth understanding of the responses that were attained from the individuals in the form of interview responses. The primary data was collected via interviews with industry employees working at British Airways. The sample size chosen for the study was 10. The interviews were conducted on Skype/Zoom platforms considering the COVID-19 situation.
3.6 Data Analysis
Data analysis is a procedure that helps in converting the raw data to the readable data for the reader (Apuke, 2017). There are various ways through which the interview responses can be analysed, such as the use of thematic analysis. Walliman (2017) described that thematic analysis as a procedure that uses texts to identify the common themes that are in line with the topic of the study. The justification for using thematic analysis for the study is that the researcher was able to identify key patterns from the interview responses and categorise them into various themes, which helped in answering the research aim and objectives of the study.
3.7 Research Limitations
This research aims to examine the direct and indirect effects of a pandemic on the air travel industry in the UK. Hence it depends on current news and business reports. Such news reports and business reviews are limited in their capacity to forecast. Therefore, the current examination’s predictions will also be limited due to unforeseen circumstances, magnified due to novel cases of the COVID-19 virus. The data collection and analysis of this study was based on a qualitative design with primary data collection in the form of interviews. Therefore, limitations inherent in this approach, such as subjectivity of the research, human biases, sample sizing, and lack of statistical representation, will be concomitant with this study as well. Moreover, subjective opinions and reviews of participants of the study created hindrances in the reproducibility of research conclusions in future, especially with regard to new developments in COVID-19 scenarios.
3.8 Ethical considerations
The ethical considerations are key areas of any research as it helps the researcher in ensuring that he has abided by all the ethical norms to ensure the credibility of the research (Ghauri, Grønhaug and Strange, 2020). For this study, the researcher abided by certain ethical norms, which made the respondents feel that they could trust the researcher. The first ethical consideration that the researcher made certain of was keeping all the personal information of the respondents in a password-protected laptop. The laptop was only accessible by the researcher, and no third party could access it. The second ethical consideration was that consent forms were signed by the respondents to ensure that each of them was part of their study by their wish and were not pressurised to be part of the study.
4. Main Findings and Conclusions
The study will assess the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic on the British aviation industry through its impacts on performance, finances, business management, and operational strategy of the industry. Through an examination of pre-pandemic compared to current operations of international aviation, it might be asserted that COVID-19 will have financial repercussions on the aviation sector. The UK aviation industry is one of the prime global operators in the field. Hence their wide network makes them particularly vulnerable to disruptions in operations in various parts of the world. Literature indicates approximately a 50%-60% drop in international air travel this year, which translates into estimated financial losses of $ 300 – 400 billion. In order to cover up the losses, the British aviation industry has developed several policies and mechanisms to screen against the pandemic and cover up financial losses in later stages in future. In this direction, some airports such as Birmingham have employed the strategy of providing maintenance checks to aeroplanes. Meanwhile, several companies have cut down their number of flights and even aeroplane fleet to cover up costs. Moreover, the glaring aspect of cost-saving vs environment also becomes prominent during this pandemic as several airline companies opt to fly their empty planes to escape the costs and taxes on parking at any particular airport. However, incessant burning of fuel and resources might induce future repercussions on the industry in the form of public discontent due to environmental and social damages. Increased screening by the aviation industry will curtail potential health and financial risks in future operations; however, ensuring the availability of basic healthcare facilities such as sanitising and travellers medical reports might be only limited in their effectiveness. This analysis might suggest the need for infrastructural redevelopment in the aviation industry for future sustainable operations, which would also make the business more inclusive and eco-friendly.
CHAPTER 4: RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Introduction
The current chapter is emphasised conducting an in-depth analysis to generate the results on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry, particularly on British Airways. The results are generated using the technique of thematic analysis that is focused on diving deeper into the research phenomena in order to gather comprehensive viewpoints from the relevant research participants to derive broader and generalised conclusions. After conducting interviews with the participants and sorting relevant data, the extracted themes are based on analysing the perception of aviation industry experts on the current pandemic of COVID-19. Other than that, findings are presented on the role of COVID-19 in raising challenges and barriers for the UK aviation sector. Additionally, consumer preferences for using airline services of British Airways during the outbreak of COVID-19 have been thoroughly reviewed. The final theme of the analysis is the impact of covid-19 on the services and operations of British Airways. Another critical component of this chapter is discussion, which is focused on comparing and contrasting the results with the reviewed literature in order to prove the research objectives proposed in the initial chapter. At last, a succinct summary is presented that highlights the major arguments from the overall analysis.
4.2 Thematic Analysis
4.2.1 Overview on the current pandemic of COVID-19
The primary theme that was generated after conducting the interviews was the overview of the current pandemic of COVID-19. In relevance to the above theme, respondent 2 shared the following viewpoint:
“I believe this epidemic of COVID-19 has caused severe fatalities in humankind across the world and confined us from physical liberty as well as social interaction.”
From the above response, it can be observed that the respondent highlighted three critical barriers raised by the outbreak of COVID-19 for the global population, which are ‘severe fatalities’, ‘physical liberty’, and ‘social interaction’. In relevance to the above statement, it has been identified that coronaviruses are a kind of virus that may infect people and cause respiratory sickness (Maneenop and Kotcharin, 2020). COVID-19 is indeed a mystery to scientists, as they only understood that the people who are afflicted with COVID-19 could transfer the disease to others before developing symptoms (Ozili and Arun, 2020). In addition, respondent 5 shared the following statement:
“I think COVID-19 is one of the deadliest viruses out there that has the capability to extend among other humans as fast as it can without showing any symptoms when spreading. The outbreak across the world caused by COVID-19 has forced people to take extra precautions while interacting with other people and maintain social distance in order to protect themselves. For almost a year, this practice has inclined us to adopt a new way of living, which is quite challenging.”
The aforementioned response from the participant specified the strength and nature of the COVID-19 virus along with the complexities caused by it that include maintaining social distance and becoming extra cautious. The above statement also indicated that COVID-19 played a crucial role in inclining people to adopt a new way of living, which contributed to creating daily-life challenges for humans. To extend the analysis, the author presents the analysis on the second theme.
4.2.2 Role of COVID-19 in raising challenges and Barriers for the UK Aviation Sector
The second theme that emerged after reviewing the interview responses was the role of COVID-19 in raising challenges and barriers for the UK aviation sector. From a broader perspective, it has been highlighted that the COVID-19 epidemic has been the most significant threat to the UK in generations, disrupting everyone’s life and having a massive economic impact. As a result, the state has undertaken extraordinary steps to limit the transmission of the virus, prevent casualties, and safeguard the NHS, all while maintaining workers employed by providing businesses with the world’s most extensive and thorough portfolio of assistance, totalling £160 billion so far (Jolly, 2020). Since the Agency’s investigation commenced, these steps have been expanded to include aviation, with the release of revised health standards and the establishment of flight hallways, which helped in the industry’s re-launch while prioritising human safety and driven by research (Nižetić, 2020). In terms of results, respondent 6 shared the following opinion:
“In my opinion, the COVID-19 pandemic has raised numerous challenges for the UK aviation sector, primarily restricting its airline services during the first few months when the virus was rapidly spreading among the people. The decision for closure of aviation service was undertaken to reduce inflow and outflow of virus within the UK.”
The above statement simply highlighted that the closure of airline services due to lockdown was one of the main challenges raised by the epidemic of COVID-19 within the UK aviation sector. In a similar aspect, respondent 3 presented the following argument:
“I believe the rise in the risk of spreading a virus during airline travel was one of the major challenges encountered by the UK aviation sector, which eventually encouraged the government of the UK to close air travel for a specific period of time.”
It can be seen from the above response that increased risk of spreading the virus was another major challenge faced by the UK aviation sector. To support the above analysis, it has been mentioned that the aviation industry has always been critical to the UK’s tactical and commercial interests. The COVID-19 contagion has resulted in a significant drop in air transport, which has proved disastrous for the economy (Nicola et al., 2020). The UK government’s aim was to identify a balanced approach to increase the frequency of flights gradually while limiting the transmission of COVID-19. However, the increased risk and rapid spread of the virus within the UK raised obstacles to achieving the aforementioned purpose (Gössling, Scott and Hall, 2020).
4.2.3 Consumer Preferences for using airline services of British Airways during the Outbreak of COVID-19
The third theme is centred on exploring the consumer preferences for using airline services of British Airways during the outbreak of COVID-19. In terms of existing literature, it was indicated that when the outbreak of COVID-19 initiated across the UK, the consumers had a specific preference for any of the airlines operating within the UK, as they were unaware of the risk associated with air travel and the spread of COVID-19 virus (Singh et al., 2020). However, as people get aware of those risks, they opt for those airlines that offer extensive protection and have robust precautionary measures against the virus (Sharma and Nicolau, 2020). Similarly, respondent 10 expanded on a prior statement by asserting that:
“British Airways was among one those airlines within the UK that was the first to adopt newly established health and safety regulations during the COVID-19 scenario. This robust adoption helped consumers in building a favourable perception of British Airways and inclined them to use airline services of this organisation amidst the COVID-19 crisis.”
In the above statement, it has been identified that the rapid adoption of new health and safety protocols by British Airways greatly contributed to developing a positive perception among the consumers for using the airline services of the aforementioned organisation. In acknowledgement of the previous viewpoint, respondent 9 provided the following statement:
“As per my knowledge, despite adaptation of health and safety protocols, many publications have reported that overall demand for air travel dropped within the UK, as the epidemic of COVID-19 drove people towards extra protection, which involved minimum use of air travel. Therefore, I think consumers had no specific perception of any airline firm, including British Airways, during the COVID-19 outbreak, as they were more focused on gathering necessary supplies for the lockdown rather than thinking of air travel.”
The above statement from one of the respondents indicated that reduced demand for air travel during the epidemic of COVID-19 diverted the attention of consumers from air travel. Therefore, they had no clear perception of any of the airline firms within the UK, including British Airways, amidst the coronavirus crisis.
4.2.4 Impact of COVID-19 on Services and Operations of British Airways
The final theme of the analysis is concentrated on examining the impact of COVID-19 on the services and operations of British Airways. From the reviewed literature, it has been identified that owing to the Covid-19 epidemic, British Airways had to slash up to 10,000 positions, despite reaching accords or arrangements in advance with its different union members (Bambra et al., 2020). The epidemic has halted years of progress in the aviation sector, causing flights to be cancelled and a recession that might last for years (Tan et al., 2020). Customers’ attitude has changed as a response to the COVID-19 crisis, travel bans, and the accompanying financial downturn, resulting in a significant decrease in demand for aircraft services (Maneenop and Kotcharin, 2020). Surprisingly, similar response has been generated from the research participants, as the respondent 5 cited:
“I highly believe that an airline firm such as British Airways was severely affected by the current epidemic of COVID-19, as it caused lockdowns and travel bans across all UK, which eventually restricted people to get the airline service.”
It can be seen from the above statement that the respondent listed travel bans and lockdowns caused by COVID-19 as major determinants that had a negative impact on British Airways in terms of revenue and sales. Another participant (respondent 7) provided the following argument:
“I think the COVID-19 pandemic had an unfavourable influence on British Airways because it reduced the revenue of the firm because of a decline in the demand for air travel during the lockdown. As reduced air travel increased operational cost of the organisation, which contributed in generating negative revenue.”
The above point of view simply identified the financial impact of COVID-19 on British Airways, as the respondent elucidated that decrease in the demand for air travel raised operational costs as well as reduced overall revenue generated by the organisation amidst the COVID-19 crisis.
4.3 Discussion
4.3.1 The theoretical concept pertaining to COVID-19 pandemic
The first objective of this research was to examine the theoretical concept pertaining to COVID-19 pandemic. From the reviewed literature, it was identified that COVID-19 is a rare virus that has been transmitted to nearly every country on the planet. The worldwide outbreak of COVID-19 has presented a severe danger to public health since it predominantly targets the respiratory system (Walker et al. 2020). The COVID-19 epidemic was regarded as one of the phenomenal challenges encountered by humanity after World War 2. The virus has migrated to every region, excluding Antarctica, ever since its discovery in China in 2019. The epidemic has been described as an extreme medical disaster as well as a historic socio-economic catastrophe (Nieti, 2020). In terms of results, it was found that the emergence of COVID-19 has generated three major hurdles for the worldwide population such as “serious mortality,” “physical confinement,” and “social distancing.” The findings also identified that the COVID-19 pandemic has been crucial in encouraging individuals to embrace a new lifestyle, which contributed to the development of multiple challenges for humans in their day-to-day operations. Moreover, it was also unveiled that COVID-19 has been one of the strongest diseases on the planet, having the capacity to transmit among people at rapid velocity without showing any symptoms. COVID-19 has created an outbreak throughout the world, forcing individuals to take additional measures when socialising with others and create social space in order to safeguard themselves.
4.3.2 The challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19
The second objective of this review was to assess the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19. From the existing literature, it was disclosed that the aviation industry in the United Kingdom has been extremely vulnerable to the COVID-19 epidemic, with the major carrier British Airways having to reduce roughly 12000 jobs to make up for the losses sustained during the epidemic (Jolly, 2020). Furthermore, huge decreases in passenger numbers have resulted in cancelled flights or empty planes flying through cities, decreasing airline revenues and causing many airlines to fire workers or go into liquidation. Some airlines have sought to discontinue reimbursing flight cancellations in order to decrease their expenses, while others have dismissed airport operators and aeroplane makers in order to conserve funds (Ozili and Arun, 2020). However, the findings highlighted that the closure of airline services within the UK due to the lockdown and the increased risk of spreading the virus were two of the most prominent challenges or barriers encountered by the aviation sector within the nation. In support of prior results, it was unveiled that the advent of the COVID-19 epidemic in late 2019 put the worldwide population in danger and hampered worldwide commercial operations in a variety of sectors. Furthermore, since the illness is quickly transferred among people, the aviation sector was one of the first industries that were affected by the incident (Nicola et al., 2020). As a result, authorities all over the world have outlawed cross-border travel, reducing the aviation industry’s entire market value (Jolly, 2020).
4.3.3 The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways
The third objective of this study was to analyse the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways. Results pertinent to the above objective highlighted that consumer behaviour has changed dramatically as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic. The COVID-19 has had a major influence on user conduct and choices. Consumer attitudes and expectations have altered as a result of the UK’s declining economic condition, with individuals losing employment at a rapid rate. People have grown more aware about how they invest their income. Although people continue to buy the essentials for life, the shopping and vacation aspects of their lives have suffered extensively (Nižetić, 2020). The findings also indicated that the pandemic has interrupted years of development at British Airways and the overall aviation industry as a whole, resulting in flight cancellations and a possible long-term depression. As a result of the COVID-19 difficulties, travel prohibitions, and the ensuing economic depression, users’ attitudes have shifted, resulting in a major drop in demand for aviation services. In terms of results from the literature, it was discovered that, given the COVID-19 epidemic, several airline companies have had to raise ticket costs in order to achieve their monthly targets. This specific feature has not gone down well with the general public (Nicola et al., 2020). Consumer attitude has changed dramatically, with consumers now deciding whether or not to spend funds on an aviation journey that is not necessary right now and may be delayed until the COVID-19 epidemic has passed (Gössling, Scott and Hall, 2020). Furthermore, Sukri et al. (2020) disclosed that tourism locations have seen a substantial drop as individuals have begun to cancel their visits owing to COVID-19 threats.
4.4 Chapter Summary
The chapter sought to present detailed results and discussion based on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry, particularly on British Airways. From the analysis, it was uncovered that the COVID-19 pandemic had raised unprecedented challenges for the overall aviation industry of the UK, which include a reduction in the demand for air travel, increased operational cost, reduced revenue, cancellation of flights, and flight delays. In terms of impact, the findings indicated that the COVID-19 outbreak had a negative impact on British Airways, as it primarily played a crucial role in increasing losses, which forced British Airways to lay off 10,000 to 12,000 employees in order to reduce operational costs. Moreover, it was also disclosed that despite the introduction of novel health and safety regulations, the use of airline services has been on the decline within the UK, which had negative implications for the services and operations of British Airways.
CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
5.1 Summarised Findings
The first objective of this research was to examine the theoretical concept pertaining to COVID-19 pandemic. According to the findings, COVID-19’s development has created three significant barriers for the global population: “severe mortality,” “physical confinement,” and “social distance.” The results also revealed that the COVID-19 epidemic was critical in pushing people to adopt a new living approach, which contributed to the emergence of various problems for humans in their daily activities. Furthermore, it was shown that COVID-19 was one of the most powerful illnesses in the world, with the ability to spread rapidly among individuals without exhibiting any indications. COVID-19 has sparked a pandemic all across the globe, requiring people to take extra precautions.
The second objective of this review was to assess the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19. The research outcomes identified that the closure of aircraft flights within the UK owing to lockdown and heightened risk of virus transmission were two of the most significant obstacles or hurdles experienced by the aviation sector within the UK. The emergence of the COVID-19 outbreak in late 2019 put the global population at risk and hindered global economic activities in a number of industries. Additionally, since the virus spreads fast among individuals, the aviation industry was one of the first to be impacted by the occurrence.
The third objective of this study was to analyse the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on British Airways. According to the results, the epidemic has disrupted years of growth at British Airways and the wider aviation sector, culminating in flight disruptions and long-term recession. Customers’ opinions have altered as a result of the COVID-19 troubles, travel bans, and the subsequent economic downturn, leading to a significant reduction in demand for air transport. Moreover, the findings also revealed that, as a consequence of the COVID-19 outbreak, some airline firms had to boost ticket prices in order to meet their quarterly targets. This particular feature has not been well received by the general population, which caused negative demand and severe impact on British Airways.
5.2 Recommendations
As the current study concentrated on examining the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the UK aviation industry. The final objective of this review was to provide recommendations for minimising the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the aviation sector of the UK. In response to the prior objective, the proposed recommendations are as follows:
- Some employment losses in the aviation industry may be unavoidable. However, such important choices concerning individuals’ careers should not be taken too soon until more data about the sector’s revival is available. Hence, it is advised to UK-based aviation businesses to postpone large-scale layoffs or changes to employment terms and benefits, as it is possible that the UK government’s proposals to revive and recover the sector would demonstrate favourable financial forecasts for the aviation firms in the near future.
- In the present situation, some layoffs at British Airways, as well as other airlines, may be unavoidable. It is believed that British Airways’ existing conversation on workforce adjustments is a determined effort to take benefit of the global epidemic to lay off workers and strengthen the contract terms of its remaining workers. Based on interviews conducted with the Chief Executive of British Airways’ parent corporation and union leaders, as well as thousands of entries from British Airways staff members. British Airways and its parent firm’s treatment of their workers is a nationwide embarrassment. It goes well short of the norms one would anticipate from any business, particularly given the size of the public support in this period of economic crisis. As a result, it is recommended that British Airways must prolong its discussion time so that all stakeholders may evaluate the planned workforce adjustments in light of the Government’s intentions to assist the aviation industry begin and thrive, as required by law.
5.3 Future Implications
The current research was carried out by using the approach of qualitative research with a purpose to analyse the challenges and barriers faced by the aviation industry of the UK due to the global pandemic of COVID-19. The analysis was carried out by using qualitative research to gather in-depth perspectives from respondents of the study. However, in the future, the research can be carried out by using quantitative methods collecting data by taking surveys from consumers of British Airways to analyse their preferences and related behaviour in the current situation of the COVID-19 pandemic. It will allow presenting factual based analysis and justifications for the recent results of this research. Additionally, comparative analysis can be performed in the future by comparing the impact of COVID-19 on British Airways and any other well-known airline like Emirates to compare their consumer preferences. Lastly, in the future, researchers can take assistance from this research who aim to gather data regarding the impact of COVID-19 on the aviation industry.
5.4 Conclusion
The global pandemic of COVID-19 has wreaked decline for a variety of sectors around the world. The current study focused on the impact of COVID-19 on the UK aviation industry, notably British Airways. The study found that the closing of borders and restrictions on local and international travel had had an impact on the UK’s aviation industry. Furthermore, the findings suggested that the global COVID-19 pandemic lowered demand for air travel by 14% in February 2020. The COVID-19 epidemic has had an impact on consumer behaviour and preferences since people are less willing to travel and prefer to stay indoors. As a result, the COVID-19 epidemic has had a significant impact on businesses, with some enterprises declaring bankruptcy and others being forced to close down. According to the study’s findings, the COVID-19 epidemic has posed major issues for a variety of industries since it has driven people to maintain social distance and avoid physical touch. Furthermore, the aviation industry is one of the few industries that has been severely impacted by the global pandemic of COVID-19 since many governments have imposed restrictions on both domestic and international travel.
Additionally, the results revealed that severe drops in traveller volumes have led to cancelled flights or unoccupied planes travelling through airports, decreasing airline profitability and causing some companies to lay off staff or liquidate its assets. Some airlines have tried to stop refunding missed flights in order to cut costs, while others have laid off-airport operations and aircraft makers to save money. British Airways is one of the major airline companies in the world, and it was severely harmed by the unforeseen COVID-19 occurrence, which prevented the UK’s aviation sector from allowing any air travel. Consumers have abandoned their plans to vacation overseas and spend a large quantity of money on plane tickets and hotel reservations. Because of COVID-19, consumer preferences have shifted, resulting in a drop in holiday expenditure. This idea is gaining traction in countries that have shown signs of recovery. In the United Kingdom, Christmas spending has decreased by 34%, with people electing to spend less or nothing until the pandemic issue is resolved. People’s behaviour has changed in the sense that they are afraid for their life because the virus has spread within a 6-foot radius. People are avoiding travel altogether as a result of this.
References
Adler, J.M., Dunlop, W.L., Fivush, R., Lilgendahl, J.P., Lodi-Smith, J., McAdams, D.P., McLean, K.C., Pasupathi, M. and Syed, M., 2017. Research methods for studying narrative identity: A primer. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(5), pp.519-527.
Amankwah-Amoah, J., 2020. Stepping up and stepping out of COVID-19: New challenges for environmental sustainability policies in the global airline industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 271, p.123000.
Apuke, O.D., 2017. Quantitative research methods: A synopsis approach. Kuwait Chapter of Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review, 33(5471), pp.1-8.
Bambra, C., Riordan, R., Ford, J. and Matthews, F., 2020. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J Epidemiol Community Health, 74(11), pp.964-968.
Barry, J.M., 2020. The great influenza: The story of the deadliest pandemic in history. Penguin UK.
Bertrand, I. and Hughes, P., 2017. Media research methods: Audiences, institutions, texts. Macmillan International Higher Education.
Brunel.ac.uk. 2020. COVID-19: The Impact On Aviation And What We Can Do About It | Brunel University London. [Online] Available at: <https://www.brunel.ac.uk/news-and-events/news/articles/COVID19-The-impact-on-aviation-and-what-we-can-do-about-it> [Accessed 11 June 2020].
Bureau, AT, 2020. Effects of Novel Coronavirus (COVID‐19) on Civil Aviation: Economic Impact Analysis. International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Montréal, Canada.
Chu, H. and Ke, Q., 2017. Research methods: What’s in the name? Library & Information Science Research, 39(4), pp.284-294.
Cox, N., Ganong, P., Noel, P., Vavra, J., Wong, A., Farrell, D. and Greig, F., 2020. Initial impacts of the pandemic on consumer behaviour: Evidence from linked income, spending, and savings data. University of Chicago, Becker Friedman Institute for Economics Working Paper, (2020-82).
Czerny, A.I., Fu, X., Lei, Z. and Oum, T.H., 2020. Post-pandemic aviation market recovery: Experience and lessons from China. Journal of Air Transport Management, 90, p.101971.
Donthu, N. and Gustafsson, A., 2020. Effects of COVID-19 on business and research. Journal of business research, 117, p.284.
Dougherty, D., 2017. Grounded theory research methods. The Blackwell Companion to Organizations, pp.849-866.
Fernandes, N., 2020. Economic effects of coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19) on the world economy. Available at SSRN 3557504.
Ghauri, P., Grønhaug, K. and Strange, R., 2020. Research methods in business studies. Cambridge University Press.
Goodell, J.W., 2020. COVID-19 and finance: Agendas for future research. Finance Research Letters, p.101512.
Gössling, S., Scott, D. and Hall, C.M., 2020. Pandemics, tourism and global change: a rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, pp.1-20.
Guo, T., Fan, Y., Chen, M., Wu, X., Zhang, L., He, T., Wang, H., Wan, J., Wang, X. and Lu, Z., 2020. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiology.
Henriques, M., 2020. Will Covid-19 have a lasting impact on the environment? BBC News.
Jamshed, S., 2014. Qualitative research method-interviewing and observation. Journal of Basic and clinical pharmacy, 5(4), p.87.
Jolly, J., 2020. British Airways Plans to Resume Some Flights in July. [Online] The Guardian. Available at: <https://www.theguardian.com/business/2020/may/07/british-airways-owner-reports-big-loss-coronavirus> [Accessed 11 June 2020].
Jones, P. and Comfort, D., 2020. The COVID-19 crisis and sustainability in the hospitality industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.
Joy, H., 2020. Lead your team into a post-pandemic world. Harvard Business Review, 8.
Kelly-Cirino, C.D., Nkengasong, J., Kettler, H., Tongio, I., Gay-Andrieu, F., Escadafal, C., Piot, P., Peeling, R.W., Gadde, R. and Boehme, C., 2019. Importance of diagnostics in epidemic and pandemic preparedness. BMJ global health, 4(Suppl 2), p.e001179.
Kumar, A., 2020. Impact of Covid-19 and what needs to be done. NOW!, 55(14), p.10.
Li, Y. and Mutchler, J.E., 2020. Older adults and the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Aging & Social Policy, 32(4-5), pp.477-487.
MacDonald, C., 2012. Understanding participatory action research: A qualitative research methodology option. The Canadian Journal of Action Research, 13(2), pp.34-50.
Mackey, A. and Gass, S.M., 2015. Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Maneenop, S. and Kotcharin, S., 2020. The impacts of COVID-19 on the global airline industry: An event study approach. Journal of air transport management, 89, p.101920.
McKinsey & Company, 2020. Consumer sentiment and behaviour continue to reflect the uncertainty of the COVID-19 crisis. [Online]. Accessed from < https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/marketing-and-sales/our-insights/a-global-view-of-how-consumer-behavior-is-changing-amid-covid-19> [4 December 2020]
Nhamo, G., Dube, K. and Chikodzi, D., 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on the Global Network of Airports. In Counting the Cost of COVID-19 on the Global Tourism Industry (pp. 109-133). Springer, Cham.
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., Agha, M. and Agha, R., 2020. The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International journal of surgery (London, England), 78, p.185.
Nižetić, S., 2020. Impact of coronavirus (COVID‐19) pandemic on air transport mobility, energy, and environment: A case study. International Journal of Energy Research, 44(13), pp.10953-10961.
Ozili, P.K. and Arun, T., 2020. Spillover of COVID-19: impact on the Global Economy. Available at SSRN 3562570.
Park, J. and Park, M., 2016. Qualitative versus quantitative research methods: Discovery or justification? Journal of Marketing Thought, 3(1), pp.1-8.
Qiu, W., Rutherford, S., Mao, A. and Chu, C., 2017. The pandemic and its impacts. Health, culture and society, 9, pp.1-11.
Rebmann, T., Wang, J., Swick, Z., Reddick, D. and delRosario Jr, J.L., 2013. Business continuity and pandemic preparedness: US health care versus non-healthcare agencies. American Journal of infection control, 41(4), pp.e27-e33.
Roy, S., 2020. ECONOMIC IMPACT OF COVID-19 PANDEMIC.
Serrano, F. and Kazda, A., 2020. The future of airport post-COVID-19. Journal of Air Transport Management, 89, p.101900.
Sharma, A. and Nicolau, J.L., 2020. An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry. Annals of Tourism Research.
Singh, S., Kumar, R., Panchal, R. and Tiwari, M.K., 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on logistics systems and disruptions in the food supply chain. International Journal of Production Research, pp.1-16.
Sukri, A.M.B.M., Razali, M.R.A.B., Yazid, N.S.B.M. and Tan, Z.Y., 2020. Interest in an Aviation Career After COVID-19.
Tan, B.Y., Chew, N.W., Lee, G.K., Jing, M., Goh, Y., Yeo, L.L., Zhang, K., Chin, H.K., Ahmad, A., Khan, F.A. and Shanmugam, G.N., 2020. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare workers in Singapore. Annals of internal medicine, 173(4), pp.317-320.
Tay, D., Du, K., Ho, J., Liu, F., Chan, C. and Cao, C., 2020. The Aviation Industry: Tackling the turbulence caused by COVID-19. IETI Transactions on Economics and Management, 1(1), pp.44-56.
Van de Ven, A.H. and Poole, M.S., 2017. Field research methods. The Blackwell Companion to Organizations, pp.867-888.
Vinod, B., 2020. The COVID-19 pandemic and airline cash flow. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, 19(4), pp.228-229.
Walker, P., Whittaker, C., Watson, O., Baguelin, M., Ainslie, K., Bhatia, S., Bhatt, S., Boonyasiri, A., Boyd, O., Cattarino, L. and Cucunuba Perez, Z., 2020. Report 12: The global impact of COVID-19 and strategies for mitigation and suppression.
Walliman, N., 2017. Research methods: The basics. Routledge.
Wire, B., 2020. Impact Of COVID-19 On The UK Economy – Researchandmarkets.Com. [Online] Businesswire.com. Available at: <https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200423005381/en/Impact-COVID-19-UK-Economy—ResearchAndMarkets.com> [Accessed 11 June 2020].
Ye, J., Ji, P. and Barthelemy, M., 2020. Scenarios for a post-COVID-19 world airline network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.02109.


