Sample Based on Sodor Project Management
Author: Ellie Cross
At: July 21, 2023
1.0 Introduction:
This paper is an exhaustive investigation of the venture of the executives of the task at the Sodor Oil Terminal, including project design and execution. Sodor is a multi-supporter activity involving numerous pupils of designing, for example, structural designing, underlying designing, mechanical designing, electrical designing, firefighting and working of planes. This incorporates a venture director who is in excess of a structural designer but has insight into different angles, for example, HR, monetary bookkeeping, time the board, combination of the executives, sourcing of cost the board and quality administration.
The paper gives a basic assessment of the association of venture authority by the group. It likewise tended to the way in which the group dealt with the task from start to finish. The instruments, techniques and systems utilized in the task are likewise examined. After the group was set up, the association of the administration of the Sodor project by team 7 started, and the real task contextual analysis was acquired multi week before the undertaking started. To effectively deal with this venture, the group began by considering the task contextual analysis and distinguished its order in this undertaking (Edum-Fotwe, 2000) .
2.1 Factors that influenced the team’s effectiveness:
2.1.1 Determination Squad
The group piece for the undertaking was left to individuals who, in light of individual inclination and inward acknowledgement, needed to sort themselves out into groups. Irregular gathering determination is extremely ordinary in an instructive setting; however not reasonable, as the assortment of abilities among understudies isn’t considered. The group that was created in this task was arbitrary as far as ranges of abilities in that there was no correlation until a group was picked, just an inclination of companions or partners. In the development of the project, this proved to be a good function (Cooke-Davies, 2001).
2.1.2 Creation for Team
Tabaka summarizing Tuckman and Jensen, recommended that the colleagues should know one another and judge their own and another part of the group in the ‘making’ measure. Locally framed for the Sodor activity, this stage was at that point achieved. As indicated by Tuckman and Jensen, the subsequent stage is ‘raging’ where colleagues endeavour to state control on one another and jockey inside the gathering for the position. At the beginning of the undertaking, this stage was at that point previously came to inside the centre group, and the group has just outperformed the ‘norming’ level of Tuckman and Jensen, with certainty developed in earlier group encounters, and the capacity to cooperate effectively has just been cultivated. The group was, in any case, prepared for the ‘performing’ phase of Tuckman and Jensens. Unfortunately, the two ‘outcasts’ of the group never acquired a genuine degree of confidence inside the group. However, they remained ‘pariahs’ for the rest of the task (Karimi Azari, 2011).
2.1.3 Plan Management Team
A significant part of the undertaking group is missing for the gatherings in the underlying periods of the Sodor project obligations. This would appear to be a fairly lamentable and negative part of the undertaking’s movement. In contrast with the groups that had procrastinated and lacked direction, Ericksen and Dyer kept up that the greater part of the dynamic venture groups they had noticed had an extremely authoritative beginning, with the sound tasks on the board, bearing and clearness directly from the start. As acknowledged in the work bargain, the other colleagues played out their (obligations in the rest of the task. It was resolved that inside the activity, the zones of pertinence would each have an individual to a great extent liable for that particular district (Kartam , 2001). Arranging, costing, sourcing, and arrangement or changing the executives were the zones of significance chosen. With little conference between individuals, the four centre individuals from the local area accepted accountability for a region, with the two ‘outside’ individuals promising to help as important. Akgun has hypothesized group measures as a method for expanding the likelihood of the culmination of an undertaking and presented the standard of ‘bunch control,’ a conviction that colleagues ought to be viable. While the Sodor group worked basically as people, there was a real certainty and a veritable conviction in the ‘power’ component among the key members, which may have been bogus (Edum-Fotwe, 2000) .
3.0 Planning and Design:
It is unimaginable to expect to overemphasize the need to give a system to the Sodor oil terminal administration. Utilizing 3M Company as a contextual analysis demonstrated that the advancement of very much characterized project needs is a critical favourable position of preparation forthright for an undertaking. The objectives help to give a group project direction. Different points of interest of arrangement incorporate; it benefits the colleagues by having unequivocally indicated jobs in the association of individual undertakings. Moreover, the task plan additionally encourages the group to give a layout of the undertaking timetable, consumptions and restrictions that would then be able to be utilized by the group as a reason for assessing genuine venture achievement (Liu, 2004) .
The planning and plan of the Sodor oil terminal started with the distinguishing proof of the information got from the venture patron of the Cost, Schedule and Scope goals. Utilizing the MS Project to make the Sodor oil terminal starter Gantt map, these objectives were then joined into a consecutive structure. A nitty gritty paper demonstrating the general spending plan, season of development, size of the undertaking, and the affirmed workers for hire picked for the task is the last Sodor oil terminal timetable. Christina showed that center components in the readiness and configuration measure that impact group execution incorporate.
Defined Goals: It has been demonstrated that the idea of explicit task expectations expands the exhibition pace of venture groups. Pinto and Slevin demonstrated that a main consideration in assessing the exhibition of groups and hence the achievement pace of tasks is very much characterized and coordinated targets. Zander proposed that groups do higher than groups with fluffy objectives with basic and perceptible objectives. This is credited to the utilization of groups of clear focuses as a premise from which group results can be evaluated. In correlation, the utilization of direct and concise needs frequently permits the group to get ready inside a particular course of events about what they will accomplish. At the start of the task, which was to deliver an undertaking plan at close to the predefined project spending given by the venture support, the needs of the Group 7 group were expressly expressed and grounded.
The Board Support: Pinto and Slevin showed that a group will, in general, advance group progress with help from the upper administration. This works by making it simple for the task group to deliver cash, accordingly guaranteeing their prosperity and assisting with disposing of regulatory bottle necks.
Multifaceted groups: It has been recommended that the significance of remembering numerous individuals for a group with different foundations positively affects group execution. Ochieng and Price have shown that the effective utilization of satisfactory intelligent techniques in a group to deliver social holes will, in general, encourage the advancement of the venture. In a group, a few networks set up people with assorted gifts, abilities, and individual characteristics focused on a shared objective. Gathering 7 multicultural atmosphere gave a pool of shifted thoughts determined by conceptualizing on which the best practicable methodology was chosen and changed over into the task plan for Sodor.
4.0 Risk management:
Distinguishing proof, measurement, response, and ultimately observing are four phases of danger the board.
For both the acquisition of materials and development, the Sodor project was absolutely dependent on outsider sellers. The powerlessness of a provider or worker for hire to perform on time will be the best conspicuous threat for the venture. This would be particularly fundamental for the exercises inside the task that were in the underlying extended timetable on the essential course. The seller assortment for these obligations ought to likewise have been painstakingly thought of. Peril is commonly measured as a component of the danger’s likelihood of the event and the result of the event. The probability is a provoking choice to make. However, scores were given to the group dependent on how reliable the supplier was. For late undertaking culmination, the outcome was the punishment rate. Only 2 were appraised by the workers for hire for the two fundamental undertakings of pier plan and construction and the establishment of channelling gear. It demonstrated to make troubles later. Obviously, it would have been costly to limit the danger by choosing better-appraised providers, which would need to be decided to be practical. In the seller choice methodology, this was incompletely considered, yet further consideration from the task the board ought to have been supported.
Another approach to manage the risk in a specific case would have been to divert it by moving it to the producers. Punishment arrangements for overwhelming the cited obligation terms ought to have been fused into their agreements. The Sodor project group was not equipped to do this, so the solitary elective left was to diminish the danger.
Monitoring:
Gannon guaranteed that project achievement can be evaluated anytime in the venture by coordinating current advancement with the underlying anticipated advancement. At 25 weeks, the slippages in the Sodor project were embedded into the Gantt guide of the venture, and it was seen that the undertaking would surpass by about a month compared with the normal because of slippage in fundamental course activities, and punishments would apply. The undertaking group has three options: embrace the punishments, abbreviate the span of an activity by paying extra time on the indispensable course.
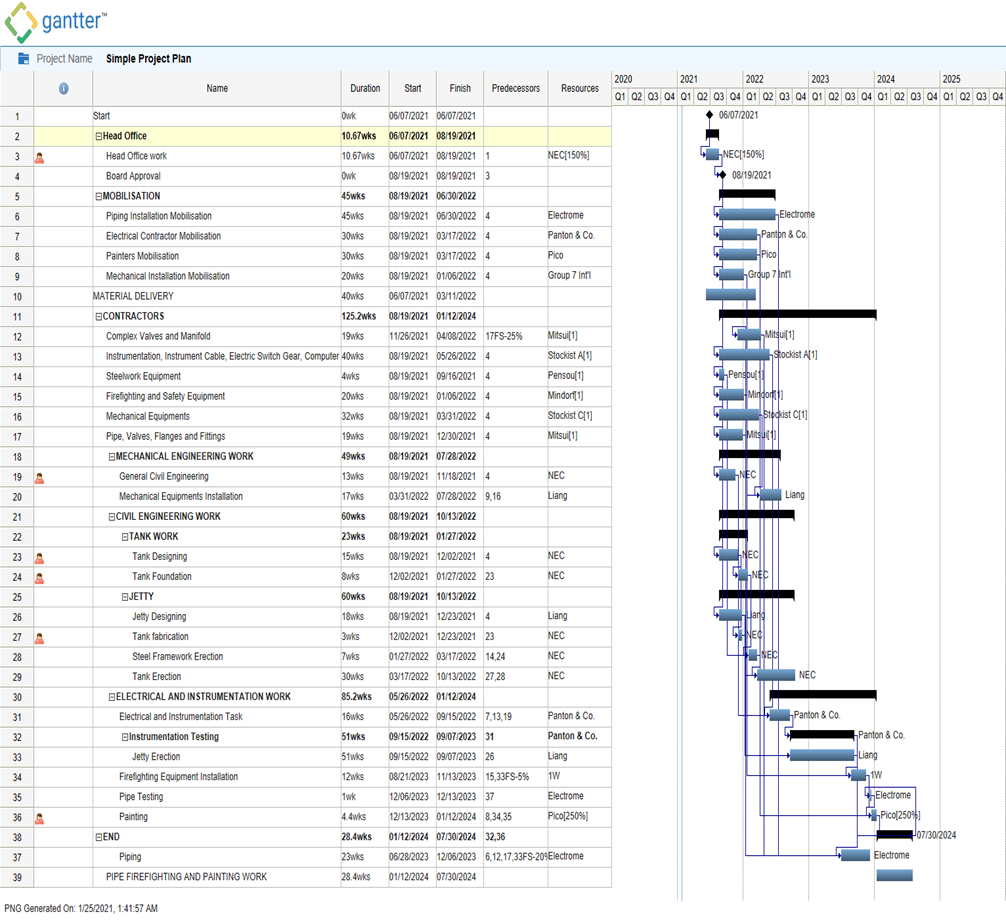
5.0 Baseline:
The underlying undertaking plan had a general task time of weeks beginning on 97.87, starting at 6 July 2021, and an expense of £ 2,234,600, and finishing on 21 April 2023.
The undertaking usage of the plan, arranging and development of the Sodor Oil Terminal started with the task group’s definition. In Session 1, Project Brief, the venture order and the power to begin the task were gotten. A paper was drawn up by the group illustrating how the group wanted to execute the proposition. The Sodor project outline has been recorded in this paper. Notwithstanding, the Project Initiation Paper [PID] precluded fundamental documentation, for example, a business case, which is an imperative archive for any task since it delineates the benefits of the undertaking. In the wake of perusing the undertaking brief and allotting assignments to the four colleagues, the group set up the task plan utilizing MS Project at the week-by-week meeting. Occupation Breakdown Structure [WBS] activity readiness mode was utilized in a hypothetically reformist way by arranging exercises. Comparable assignments were frequently bunched for each stage under indicated stage headings with clear terms. Nonetheless, there was no data about providers and contract-based workers at this stage, so the asset use sheet in the MS venture couldn’t be loaded up with complete undertaking information. A benchmark has been put something aside for the venture plan (Graham,1999). To oversee, control and track the venture, the benchmark is fundamental. In view of the information introduced in the brief in Session One, the undertaking plan was created. Assignments, their expenses and estimated length in weeks and the request wherein such errands were to be finished were the subtleties introduced. The capacities and their archetypes were allotted in their consecutive request. Such cutoff times, for example, ‘Undertaking Launch’,’ Board Acceptance’ and ‘End of Project’, were likewise allotted to the task plan.
The task plan was saved as ‘Meeting 1.1-Original Benchmark’ for a ‘Unique Baseline’ was done. The group built up the Cost Model and a Critical Path from the saved undertaking plan that were caught against the underlying benchmark. Notwithstanding, it was not practical to choose if the expense was past the assigned financial plan if there was no spending plan apportioned. With project stages alluded to as stages that permit the venture supervisor to deal with the task, the last undertaking was planned (Edum-Fotwe, 2000).
5.0 A Project Closure
An examination of the last Sodor terminal task intended to guarantee the scale, cost and timetable cutoff times were reached was remembered for the nearby out stage. The paper gained from the exercise was then set up to exhibit the various clashes that existed during the undertaking and how the group dealt with them to incorporate exercises for what’s to come. The last task proposition was then introduced to the patron of the venture, and the Project Manager disfigured Community Group 7 . We had the option to accomplish a last undertaking cost of £ 2,754,600 and 94.47 weeks and 13,600 hours. The close-out closed earlier, at 3.4 weeks and 1,080 hours (Gannon, 1984).
6.0 Conclusion:
The Sodor project was a colossal task, including multi-discipline groups that elaborate a ton of group gatherings on the field. Yet, the group had extremely restricted contact with the creation groups in the present circumstance. The nonattendance of a spending plan was a critical stream in this task since three things that are followed are cost (financial plan), time and unpredictability (highlights objectives) for the venture group to deal with the undertaking progress. The group didn’t do an extensive advantage investigation plan, so the undertaking was driven exclusively by the degree and length. It is suggested that a particularly significant exercise ought to be done in a close. The undertaking brief proposed that the Project Manager was knowledgeable in underlying designing, steel works, and electrical works, which couldn’t be the situation. Eventually, before the task started, the primary execution measurements more likely than not been caught. At one or the other purpose of the task, these will be debilitating guidelines. It will likewise assist with following and incorporate the important and proper controls to keep the venture on course. Equipped venture, the board is prescribed to be given to tasks of such size. The utilization of talented development projects on the board, known as Construction Supervision (CS), was actualized in 1998 because of the fast development of the development business in China (Liu, 2004).
Appendix 1- Baseline
Appendix 2-Closeout:

6.0 References:
- Ahola, T., Ruuska, I., Artto, K., and Kujala, J., 2013. What is project governance, and what are its origins? International Journal of Project Management.
- Akintoye, A., MacLeod. and M, J., 1997 . Risk Analysis and Management in Construction International Journal of Project Management Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 31-38 .
- Atkinson, R., 1999. Project management: cost, time and quality, two best guesses and a phenomenon, its time to accept other success criteria, International Journal of Project Management Vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 337-342.
- Cooke-Davies, T., 2002. The ‘‘real’’ success factors on projects International Journal of Project Management 20 pp.185-190.
- Edum- Fotwe, F.T., and McCaffer, R., 2000. International Journal of Project Management 18 pp. 111-124 Developing project management competency: perspectives from the construction industry.
- Gannon., 1984. Effects of project governance structures on the management of risks in major infrastructure projects: A comparative analysis, International Journal of Project Management 32 pp. 815– 826.
- Hosseini, M. R., and Chileshe, N., 2013. International Journal of Project Management 31 pp. 1101 – 1117 Global virtual engineering teams (GVETs): A fertile ground for research in Australian construction projects context.
- Hwang, B., Zhao, X., and Toh, L.P., 2014. Risk management in small construction projects in Singapore: Status, barriers and impact, International Journal of Project Management 32 pp. 120
- Kaiser, M.G., Arbi, F.E., and Ahlemann, F., 2014. Successful project portfolio management beyond project selection techniques: Understanding the role of structural alignment International Journal of Project Management
- Karimi Azari, A., Mousavi, N., Mousavi, S, F., and Hosseini, S., 2011. Risk assessment model selection in construction industry Expert Systems with Applications 38 pp. 9105-9111
- Kartama, N.A., 2001. Corresponding author contact information, E-mail the corresponding author, Saied A. Kartamb Risk and its management in the Kuwaiti construction industry: a contractors’ perspective International Journal of Project Management Volume 19, Issue 6, August 2001, pp. 325 –335
- Liu, G., Shen, Q., and Shen, L., 2004. Factors constraining the development of professional project management in China’s construction industry, International Journal of Project Management 22 pp. 203– 211.
- Ljevoa, Ž., and Vukomanoviü, M., 2014. Project Management practised in Public Project Stream of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences 119 pp. 692 – 701.
- Lyons, T., and Skitmore, M., 2004. Project risk management in the Queensland engineering construction industry: a survey International Journal of Project Management 22 pp.51– 61
- Pheng, S., 1998. Back to the basics: biblical wisdom for effective construction project management, Low International Journal o/’ Project Management Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 209 214,
- Sambasivan, M., and Soon, Y.W., 2007. Causes and effects of delays in Malaysian construction industry, International Journal of Project Management 25 pp. 517 – 526.
- Shehu, Z., Endut, I,R., and Akintoye, A., 2014. Gary D. Holt Cost overrun in the Malaysian construction industry projects_ A deeper insight, International Journal of Project Management.
- UK Essays. November 2018. The Sodor Oil Terminal.


