Evolution of Cloud Computing – Benefits of Amazon Web Services to SMEs in the UK
Author: Ellie Cross
At: July 20, 2023
| 1: Introduction – Defining the Scope of the Project (maximum 100 words) |
| Outline the Entrepreneurship/Business issue you wish to research as precisely as you can. Since 2000, cloud computing has been widely implemented by different large tech-corporation to offer on-demand online system resources, especially data storage and computing performance, without any direct active management required from the user. Technically, cloud computing is a cloud-based software infrastructure that facilitates the access of application and data on remote servers from any devices worldwide with an internet connection (Velte, Velte and Elsenpeter, 2009). This means that cloud computing makes it possible to store files in a secure remote database and make them available to retrieve instantly on demand. Amazon Web Service was established in 2006, offering businesses scalable cloud storage to build a secure digital infrastructure. With Amazon being a megacorporation in technology, the AWS will guarantee their clients from data breach (Amazon, 2006). However, many small businesses have not realised the potential benefits that these services could offer in the long term. Therefore, this research aims to explore how AWS could be beneficial to SMEs in the UK and ultimately enlighten businesses about AWS. References: Velte T, Velte A, Elsenpeter R. Cloud computing, a practical approach. McGraw-Hill, Inc.; 2009 Sep 22. Amazon, 2006. Amazon Web Service. [Online] Available at https://aws.amazon.com/. [Accessed on 01/01/2021] |
| 2: Critical Literature Review and reference list (maximum 750 words excluding references) |
a. The implication of cloud computing in business growth The concept of cloud computing has its origin in other technologies, including fundamental internet, multi-core chips, and coordinated and distributed systems (Ambrust et al., 2010). Numerous small-medium enterprises nowadays are still having difficulty adapting to marketplace changes and responding to new trends due to their ineffective technological structure (Marston et al. 2011). Therefore, cloud computing services offer a much more scalable and reliable IT infrastructure which is specifically designed to enhance business performance and future growth. Madhavaiah and Bashir (2012) stated that business could guarantee reliable emergency recovery and backup solutions since the data stored in the cloud is mirrored across the server. It means that if one fails, data will instantly backup to another remote server and the business could still retrieve the data immediately as usual. This would minimise website downtime and loss of productivity even if there is a failure in the cloud storage network. Devasena (2014) also pointed out that having an auto backup digital storage would not only boost the business growth but also minimise time consumed and operating costs. Devasena’s perception was supported by Vasiljeva, Shaikhulina and Kreslins (2017), who observed through their research that by utilising remote servers, businesses could save overhead costs such as storage equipment, software updates and setup costs. They also realised that there has been a huge increase in small-medium enterprises beginning to recognise the benefits of cloud computing. The cloud service models normally are deployed to clients through four main delivery methods based on demand, number of users, security, and privacy concerns. Studies have affirmed that these delivery models are public, private, hybrid and community clouds (Chen and Deng, 2009; Dikaiakos et al. 2009). In the public cloud, a third party would own most of the physical resources and then provides cloud services to multiple users through the internet. Meanwhile, the private cloud service is offered solely to a specific organization and mostly constrained by the desire to gain complete control of corporate data, security guidelines and system performance (Rittinghouse and Ransome, 2016). They also raised that an enterprise could absolutely set up its own cloud services, and a third-party service could be contracted to manage the operation on its behalf. Furthermore, the cloud services could reside off or on the premises of the enterprise. A community cloud service is offered to a specific group of enterprises having a similar missions, security policies, and compliance conditions (Furht, 2010). The community cloud deployment is perceived as a rationalization of the private cloud, hence having more than one enterprise in operation (Luo et al. 2011). However, Baciu’s studies claimed that not all cloud network providers are created equally, which results in limited functionality, loss of control and detrimental technical issues that could potentially lead to data breaches. Accordingly, Avram (2014) also criticised that enterprises’ data could be exploited by the cloud provider for marketing purposes or perhaps government intrusion. These perspectives demonstrate the potential benefits of adopting cloud computing but also consider the downsides in terms of confidentiality and reliable provider. Hence, a further literature review has been conducted to determine why Amazon Web Service is probably the best cloud storage provider for small-medium enterprises. b. Amazon Web Service functionalities and perceived benefits for SMEs Amazon Web Services (AWS), which provides cloud computing and other services today, was founded back in 2002 (AWS, 2021). At that time, it was providing only a few services and tools. In 2006, it re-launched its services and started providing three of its key service-based platforms, namely, S3 cloud storage, Amazon SQS, and Amazon EC2 (AWS, 2021). Presently AWS offers a wide range of cloud computing services to its users (AWS, 2021). AWS offers a higher performance and more comprehensive cloud services platform with numerous different functionalities aiming to help business scale and grow. AWS currently possess the highest market share among the world’s top providers of cloud service platform (Google, Microsoft, etc) for businesses (Varia and Mathew, 2014). In particular, object storage is for application involving flexibility and collaboration that is applied to import existing information for analytics, backup, or archiving. File Storage, i.e. the Elastic File System (EFS), is for applications that require access to shared files such as large content depositories, company directories and developmental environments. Block Storage, i.e. Elastic Block Store (EBS), is for applications consisting of large databases and ERP systems which often demand devoted and low latency storage. Amazon EBS is used to provide storage for EC2, a virtual machine hosting to support compute space in the cloud (Murty, 2008).  |
| 3: Research questions and/or hypotheses (maximum 150 words) |
| Identify research questions (and research hypotheses if necessary) which will guide your research. Show how these link to the main themes from your literature, if possible, through the use of a conceptual framework The following hypotheses are intended to be explored upon completion of this study. RQ1) Cost savings (due to scalability of resources and minimal physical storage equipment) has a positive impact in terms of accessibility and convenience for SMEs. RQ2) Reliability and mobility achieved using digital files and documents, which can be delivered through a cloud network (compared to physical assets), improving collaboration RQ3) What are the benefits of using Amazon SQS and EC2 services by SMEs in the UK? |
| 4: Research Methods (maximum 500 words) |
| Identify as precisely as you can your intended methodology and research design and the methods that you intend to use. Reference should be made to academic literature. You should also identify possible data and discuss issues associated with access (for example, how you intend to recruit participants). In this proposed study, the primary quantitative research method is intended to be used, where Positivism (positivist) research philosophy, deductive approach, and survey design are intended to be used in line with the Onion Research framework given by Saunders (2011). Gratton and Jones (2010, p. 26) suggested that quantitative research and positivist research are deductive in nature. Saunders (2011, p. 133) suggested that “the positivist paradigm prescribes quantitative methods”. However, Gratton and Jones (2004, p. 36) suggested that “Inductive research is more often associated with interpretative, qualitative studies.” As the intended method to conduct this study was quantitative, therefore, positivist research philosophy will be appropriate to select. Consequently, the selection of positivist research philosophy, deductive approach, and survey designs/strategies are backed by the literature. In deductive research, the quantitative data is collected, and the data is analyzed quantitatively to statistically test the developed hypotheses. Therefore, in this study, the quantitative data will be collected by conducting an online survey to collect quantitative responses from a sample of 50 managers working in the SMEs in the UK, which have been using the cloud-based platforms of AWS, were selected as the research sample. There were different research designs which can be selected to complete this study, such as; case study design, grounded theory design, experimental design, and survey design, as per Saunders, Lewis, and Thornhill (2012). This study it is intended to collect quantitative data from the managers working in UK SMEs using the cloud-based platforms of Amazon Web Services. Therefore, the selected design is a survey design. So the target population of this study is comprised of managers working in the SMEs in the UK, which have been using the cloud-based platforms of Amazon Web Services. The snowball sampling technique will be used to reach the target sample of 50 participants. The online open-ended questionnaire will be developed on Google Forms, and its link will be shared with a first manager working in the UK SMEs using the cloud-based platforms of Amazon Web Services. The manager will then refer the link to another manager (respondent), and this chain of referrals will go on until the desired sample size reaches. The participants will self-administer the questionnaire, and it will take 5 to 10 minutes to complete each questionnaire. The questionnaire will be based on a Likert-type scale, and the collected data will be analyzed using descriptive statistical analysis on SPSS (Field, 2013). References: Field, A. (2013). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics. New York, SAGE. Gratton, C., & Jones, I. (2004). Research Methods for Sport Studies, 1st Edition. London: Routledge. Gratton, C., & Jones, I. (2010). Research Methods for Sport Studies. Taylor & Francis. Saunders, M. N., Lewis, P. & Thornhill, A. (2012). Research Methods for Business Students. London: Pearson. |
| 5. Timeline |
Insert or attach a timeline including all elements of your research project(e.g. in the form of a Gantt chart)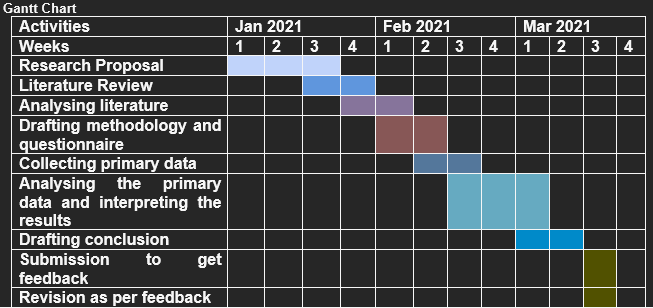 |
| Final submit |
| 6: Ethics |
| You must also submit a completed Research Ethics form, either NBS Ethics02 or NBS Ethics03, and any required participant information and consent forms with this document. Please note that you CANNOT start collecting data until your ethics form has been signed off by your supervisor. I confirm that I have submitted NBS Ethics03and Participant consent form with my research proposal. |


